Imagine moving an entire skyscraper, with all the people still inside. That’s the level of precision and reliability zero-downtime migration demands in modern tech environments.
Zero-downtime migration allows organizations to update infrastructure, refactor architecture, or move to the cloud without users experiencing a single blip in service. In today’s always-on economy, it’s not just a technical upgrade; it’s a business-critical capability.
Why Zero-Downtime Migration Matters More Than Ever
Zero-downtime isn’t just a DevOps buzzword; it’s a competitive necessity in today’s digital landscape. Here’s why:
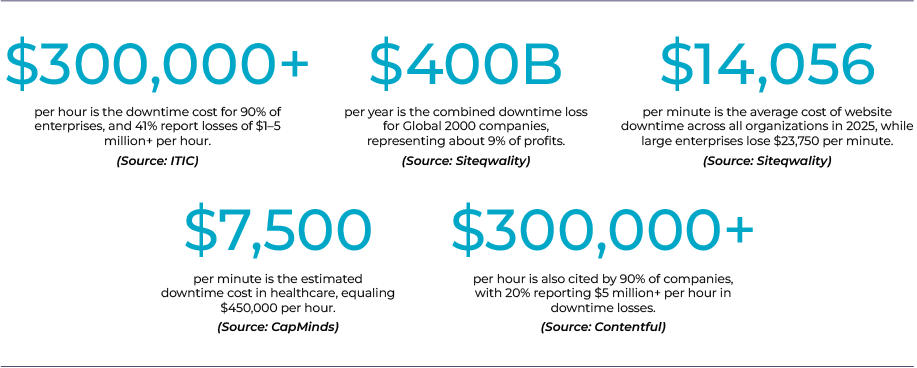
1. Uptime Is the New Brand Value
For customer-facing applications (think fintech, e-commerce, or SaaS), availability equals credibility. Downtime, even for minutes, translates to lost transactions, broken trust, and damaged brand equity.
2. Global and Remote Operations Never Sleep
Teams operate across time zones. Systems support users 24/7. You can no longer rely on “scheduled maintenance windows” when your platform never sleeps.
3. Compliance and SLA Enforcement
Regulated industries (banking, healthcare, telecom) often have strict uptime requirements and non-negotiable SLAs. Any downtime can incur legal and financial penalties.
4. Data Integrity and Real-Time Sync
Modern systems rely on distributed databases and microservices. During migration, even milliseconds of replication lag can lead to data conflicts, inconsistencies, or lost writes. Zero-downtime strategy ensures lossless, synchronized transitions.
5. Cost of Downtime Is Sky-High
A Gartner study estimates that downtime costs enterprises an average of $5,600 per minute. Beyond the financial impact, engineering stress, recovery delays, and customer support spikes exacerbate the situation.
Key Strategies That Make Zero-Downtime Migration Work
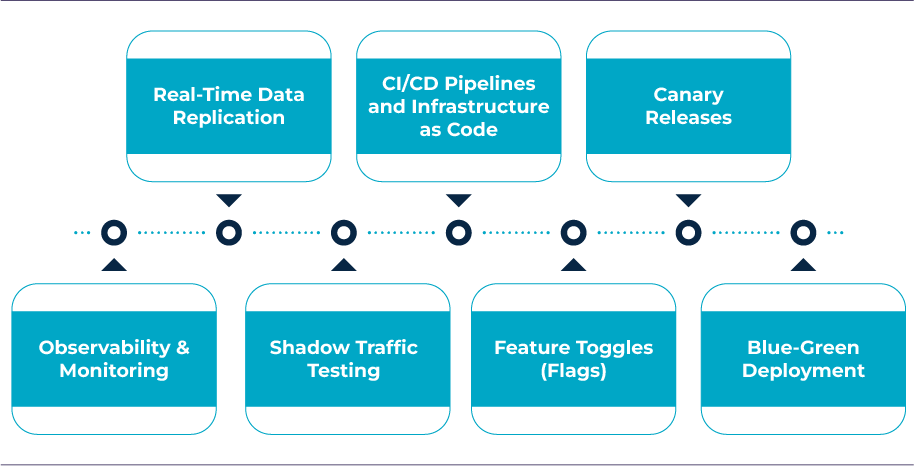
1. Blue-Green Deployment
Maintain two environments: “blue” (live) and “green” (new). Deploy changes to green, test extensively, then reroute traffic. If things go wrong, just route back to blue. It offers immediate rollback with minimal user risk.
2. Canary Releases
Gradually roll out features or environments to a small percentage of users. Monitor their behavior, gather metrics, and scale the rollout once confidence is established. This method reduces the blast radius.
3. Feature Toggles (Flags)
Enable or disable features in production without deploying new code. They allow for A/B testing, phased rollouts, and safe experimentation.
4. CI/CD Pipelines and Infrastructure as Code
Automated pipelines ensure repeatable, consistent deployments. Combined with tools like Terraform or Ansible, teams can script infrastructure and avoid manual errors during migration.
5. Shadow Traffic Testing
Mirror production traffic to the new system to test its behavior under real-world conditions. It’s especially useful when validating performance, scalability, or new architecture.
6. Real-Time Data Replication
Ensure your legacy and new environments stay in sync during the migration. Use event-based systems like Kafka, or DB tools like Debezium for log-based change capture.
7. Observability and Monitoring
Use modern observability stacks (Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog, OpenTelemetry) to capture metrics, logs, traces, and alerts. Detect and act on issues before users report them.
Real-World Use Cases

Uber
Rebuilt its trip fulfillment platform without impacting active services. They introduced city-level metrics, comprehensive integration testing, and progressive migration strategies to ensure seamless operation.
Symantec
Migrated its mission-critical workload to Azure Cosmos DB with zero downtime. Focused on high availability, elastic scaling, and precise workload partitioning.
Delivery Hero
Used shadow testing and phased API replacement for a global API migration. Their method avoided service disruption and improved performance globally.
Cost Advantages
While zero-downtime migration may require temporary double infrastructure (e.g., running parallel environments), the long-term savings include:
- No Lost Sales or SLA Penalties: By avoiding even short periods of downtime, businesses prevent lost transactions and avoid costly SLA violations that could damage customer relationships.
- No Emergency Recovery Costs: Rollback strategies reduce the need for expensive, reactive firefighting after failed deployments.
- Reduced Churn Due to Stable Experience: Users remain satisfied and loyal when they aren’t disrupted, reducing the cost of acquiring new users.
- Improved DevOps Efficiency Through Automation and Tooling: Once set up, zero-downtime frameworks streamline future deployments, reducing manual labor, overtime costs, and deployment failures.
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Better monitoring, streamlined rollouts, and reduced post-deployment fixes lead to fewer long-term maintenance costs.
- Increased Developer Productivity: Engineers can release features without waiting for downtime windows, accelerating delivery cycles and maximizing development ROI.
Final Thoughts
Zero-downtime migration is where strategy meets engineering precision. It requires careful orchestration of infrastructure, code, and user experience. But when done right, it allows businesses to innovate rapidly without losing momentum or trust.
At Murkez Technologies, we enable seamless, interruption-free migrations for cloud, database, and architecture transitions. With deep expertise in DevOps, automation, and real-time systems, we ensure your users never see the wires behind the upgrade.
Whether you’re scaling globally, modernizing infrastructure, or making the leap to microservices. Murkez delivers zero-downtime, zero-fear migrations.